Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa Vara-pericarditis Syndrome
Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome. Coxa vara deformity or other dysplasia associated with progressive hip disease may develop over time. This gene is responsible for making a protein that lubricates the jointsThe condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. The syndrome encompassing the combination of pericarditis arthritis and camptodactyly is a rarely described cause of pericardial constriction in children.
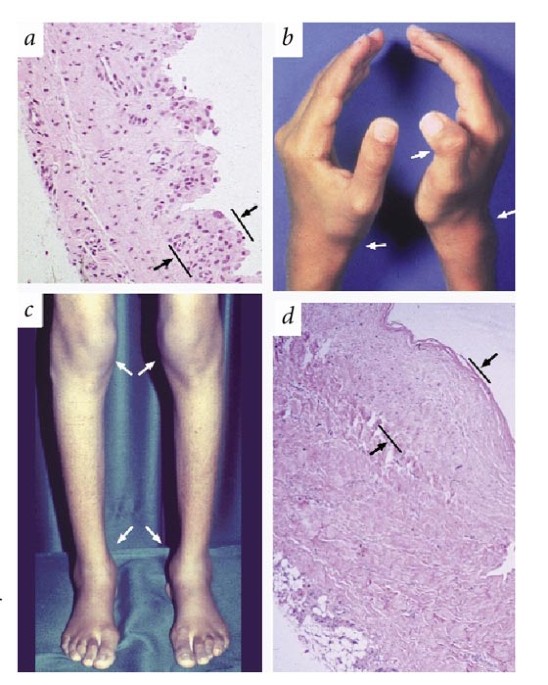
A syndrome that is characterized by congenital or early-onset camptodactyly noninflammatory arthropathy with synovial hyperplasia and in some patients progressive coxa vara deformity andor noninflammatory pericardial or pleural effusion that has_material_basis_in autosomal recessive inheritance of homozygous mutation in the proteoglycan 4 gene PRG4 on. Disease - Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome Map to. A locus responsible for.
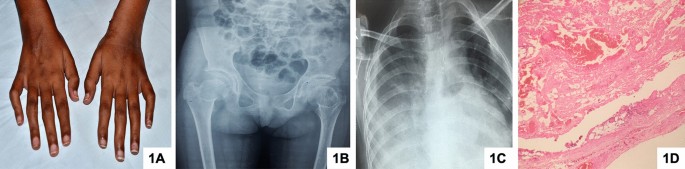
CACP may be at first confused with juvenile idiopathic arthritis because the two diseases have similar symptoms. The camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis CACP syndrome is a rare congenital autosomal recessive disorder caused by mutations in the PRG4 gene. Clinical pericarditis may also occur.
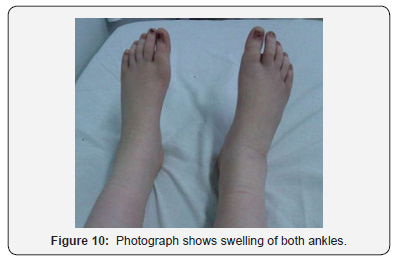
The principal features of the CACP syndrome are congenital or early-onset camptodactyly and childhood-onset noninflammatory arthropathy. Children with CACP syndrome suffer from congenital camptodactyly arthropathy coxa vara and sometimes pericarditis. Individuals with CACP have normal.
CACP syndrome is characterized by early onset camptodactyly non-inflammatory arthropathy synovial hyperplasia and progressive coxa vara deformity. A rare genetic disorder has been recognized and termed camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome CACP syndrome. Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome CACP is an autosomal recessive disorder that mostly affects joints and tendons but can also affect the pericardium and pleura which are the surfaces that surround the heart and lungs respectively.
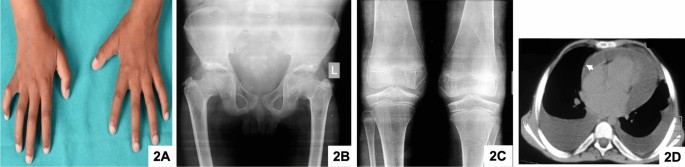
Camptodactyly - Arthropathy - Coxa Vara - Pericarditis Jacobs Syndrome. Coxa vara deformity or other dysplasia associated with progressive hip disease. We report a new case in which the skeletal abnormalities were subtle.
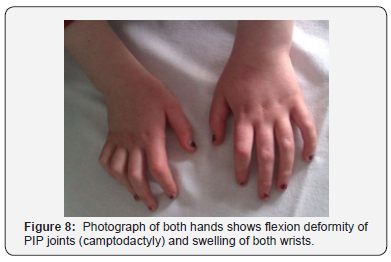
Camptodactyly arthropathy coxa vara pericarditis CACP syndrome is a rare condition principally characterized by. Camptodactyly-Arthropathy-Coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome AJR185 August 2005 523 inflammation such as heat coxa vara reduc-tion of the angle between the femoral neck and shaft and pericarditis as a distinct syndrome 3 albeit with much clinical variability 4.
An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by the association of congenital or early-onset camptodactyly and non-inflammatory arthropathy with synovial hyperplasia.
Clinical pericarditis may also occur. Congenital or early-onset camptodactyly and childhood-onset non-inflammatory arthropathy. Al-though the gene has not been identified it has. It is a non-inflammatory arthropathy characterized by joint effusions and synovial hypertrophy. CACP syndrome is characterized by early onset camptodactyly non-inflammatory arthropathy synovial hyperplasia and progressive coxa vara deformity. An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by the association of congenital or early-onset camptodactyly and non-inflammatory arthropathy with synovial hyperplasia. A rare genetic disorder has been recognized and termed camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa vara-pericarditis syndrome CACP syndrome. Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa Vara-Pericarditis Syndrome Versus Juvenile Idiopathic Arthropathy - PubMed CACP syndrome should be considered in all patients who present with a noninflammatory arthropathy or with atypical juvenile idiopathic arthritis particularly if radiographs reveal an absence of erosions. Clinical pericarditis may also occur.
It is a non-inflammatory arthropathy characterized by joint effusions and synovial hypertrophy. CACP may be at first confused with juvenile idiopathic arthritis because the two diseases have similar symptoms. The camptodactylyarthropathycoxa varapericarditis syndrome CACP is an autosomal recessive condition characterized by the association of congenital or early onset camptodactyly and noninflammatory arthropathy with synovial hyperplasia. This gene is responsible for making a protein that lubricates the jointsThe condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. The syndrome encompassing the combination of pericarditis arthritis and camptodactyly is a rarely described cause of pericardial constriction in children. An autosomal recessive disorder characterized by the association of congenital or early-onset camptodactyly and non-inflammatory arthropathy with synovial hyperplasia. Children with CACP syndrome suffer from congenital camptodactyly arthropathy coxa vara and sometimes pericarditis.



























Post a Comment for "Camptodactyly-arthropathy-coxa Vara-pericarditis Syndrome"